1.Introduction
Coconut trees and beetle nut palms are the most common palm plants which mainly distribute in tropical areas in China. With the frequent exchanges of goods in international trade, an important, destructive insect pest – coconut leaf beetle (Brontispa longissimaGestro) were found to invade Hainan Province of China in 2002. By the end of 2004, coconut leaf beetles have spread to the whole southern provinces in China including Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Fujian, and parts of Yunnan Province. The growth of damaged coconut palm and betel nut palm is inhibited, and production reduced. Some trees may even die when damages are serious. Coconut leaf beetles which caused huge economic loss and landscape destruction has become a new ecological disaster gradually.
1.1. Damage Symptoms of Coconut leaf beetles
Coconut trees and beetle nut palms are the most common palm plants which mainly distribute in tropical areas in China. With the frequent exchanges of goods in international trade, an important, destructive insect pest – coconut leaf beetle (Brontispa longissimaGestro) were found to invade Hainan Province of China in 2002. By the end of 2004, coconut leaf beetles have spread to the whole southern provinces in China including Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi, Fujian, and parts of Yunnan Province. The growth of damaged coconut palm and betel nut palm is inhibited, and production reduced. Some trees may even die when damages are serious. Coconut leaf beetles which caused huge economic loss and landscape destruction has become a new ecological disaster gradually.
1.1. Damage Symptoms of Coconut leaf beetles



Damage symptoms
Damaged king palm
Damaged Coconut Grove
Coconut leaf beetle is the most serious insect pest in palm plant industry and its related industries. The damaged coconut trees and areca nut trees usually reduce more than 60% of the production. In addition, it has destroyed the ecological landscape and environment in the regions
.
1.2. Distribution of Coconut leaf beetles
.
1.2. Distribution of Coconut leaf beetles
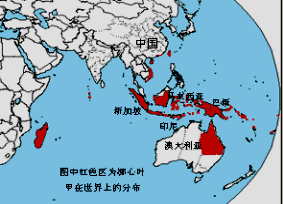
The coconut leaf beetle is distributed in more than 20 countries or regions, including China (including Taiwan, Hongkong, Hainan, Guangdong, Guangxi), Indonesia, Australia, Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, New Caledonia, Samoa, French Polynesia, New Hebrides islands, the Bismarck islands, Society Islands, Tahiti, Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and Laos.

The morphology of coconut leaf beetle at different developmental stages
2.The parasitic wasps of coconut leaf beetles
The parasitoids of coconut leaf beetles are including egg parasitic wasps, such asHaeckeliana brontispaeFerriere,Trichogrammotidea nana(Zehntner), andOoencyrtussp., and larva and pupa parasitic wasps, such asAsecodes hispinarumandTetrasticbus brontispaeFerrire. Among of these, the most important parasitic wasps areT. brontispaeandAsecodes hispinarumBoucek.
The parasitoids of coconut leaf beetles are including egg parasitic wasps, such asHaeckeliana brontispaeFerriere,Trichogrammotidea nana(Zehntner), andOoencyrtussp., and larva and pupa parasitic wasps, such asAsecodes hispinarumandTetrasticbus brontispaeFerrire. Among of these, the most important parasitic wasps areT. brontispaeandAsecodes hispinarumBoucek.


The morphology ofTetrastichus brontispaeFerrire
The morphological characteristics, developmental period, mating behavior, parasitic behavior, parasitic rate, sex ratio, selectivity of host age, parthenogenesis and degradation of these two parasitoids, were observed systematically. The effects of the environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, illumination, nutrition compensatory, on the growth, breeding and offspring quality of these two parasitoids have been studied. Population characteristics, large scale propagation and suitable releasing conditions of two parasitoids have also been explored. And their behaviors in suitable distribution area in China have also been analyzed.
3.Large scale production technology
3.1. Artificial rearing of coconut leaf beetles and its semi-artificial forage
3.Large scale production technology
3.1. Artificial rearing of coconut leaf beetles and its semi-artificial forage
.png)
The trials of parasitoids breeding, such as feeding equipment selection, collections of different growth stages of coconut leaf beetles, rearing density, replacement time of feed, time and proportion of wasp vaccination, collection and conservation of muscardine cadavers, degradation and rejuvenation of female wasps, propagation conditions and cost of parasitoids, were conducted. Semi-artificial forage of coconut leaf beetle has been developed successfully based on ingestion, nutrient component, effectiveness evaluation, type and formulation.
3.2. Artificial breeding technique of parasitic wasps
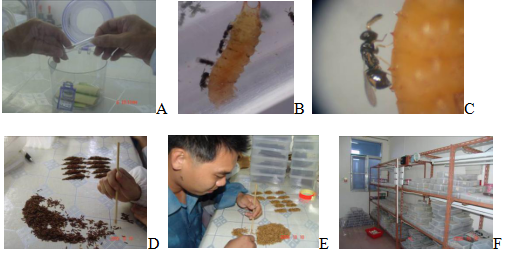

Large scale propagation technologies ofA. hispinarum,T. brontispae, and coconut leaf beetle, have been developed. These technologies reduced the costs of breeding parasitic wasps down to 0.005 yuan per oneA. hispinarumand 0.01 yuan per oneT. brontispae.
3.3.Industrialized production

Four breeding plants were built at Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences, including Environment and Plant Protection Institute, Coconut Research Institute, Hainan Forestry Science Research Institute, Forest Pest Control and Quarantine Station of Danzhou City. More than 1.5 million ofA. hispinarumand 500 thousand ofT. brontispaeare produced every day averagely.
4.The demonstration and application of parasitoids
This technique, using two parasitoids to control coconut leaf beetles, has been applied to five provinces and regions in tropical areas in China. The accumulated application area is about 1.13 million ha, which have saved economic loss of more than 3.1 billion yuan in all. The social, ecological and economic benefits are very prominent.
4.The demonstration and application of parasitoids
This technique, using two parasitoids to control coconut leaf beetles, has been applied to five provinces and regions in tropical areas in China. The accumulated application area is about 1.13 million ha, which have saved economic loss of more than 3.1 billion yuan in all. The social, ecological and economic benefits are very prominent.
EPPRI scientists developed a releasing device of parasitic wasps that is simple, convenient to manufactures. And this kind of releaser is also very cheap, effective to cover from rain, and strong stability of suspension. AS compared with test tube releasing method in foreign countries, the manpower and material resources are saved and the control effect is improved.

Tracking survey after release

Technology demonstration and application

Comparison between before and after release
This invent has been authorized a special award by Hainan Provincial Science and Technology Deparment. At present, these technologies have been applied to the coconut tree distribution areas in China, and also transferred to Maldives in 2014.

Patent and awards

Applications in Maldives


